この記事では、統計学やデータ分析の初心者に向けて、「名義尺度」「順序尺度」「間隔尺度」「比例尺度」という四つの基本的な尺度について、より分かりやすく解説します。これらはデータの種類を分類し、どのようにデータを扱うかを決定するのに役立ちます。まずは、それぞれの尺度が何を意味するのか、具体的な例とともに見ていきましょう。
名義尺度とは?
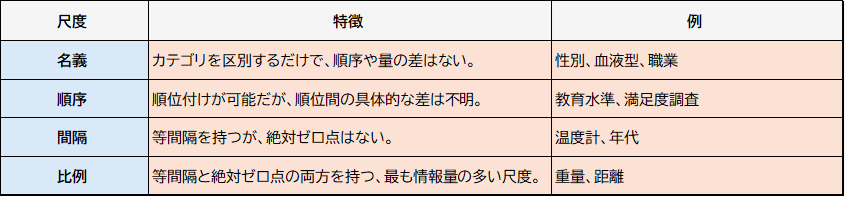
名義尺度とは、データを分類するために使う尺度です。この尺度では、データにつけた数字は、そのデータがどのグループに属しているかを示すだけで、数字の大きさや順番には意味がありません。例えば、次のようなデータは名義尺度です。
性別(1=男性、2=女性)
血液型(1=A型、2=B型、3=AB型、4=O型)
職業(1=教師、2=医師、3=エンジニア)
このようなデータは、単純に分類したいときに使います。例えば、アンケートで人の職業を聞いたり、動物を種類ごとに分けたりするときなどです。
順序尺度とは?
順序尺度とは、名義尺度よりも少し情報量が多く、データに順番やランキングができる尺度です。この尺度では、データにつけた数字は、そのデータがどのくらい高いか低いかを示します。しかし、数字の間の差は一定ではないので、数字の大きさには注意が必要です。例えば、次のようなデータは順序尺度です。
教育水準(1=高校卒、2=大学卒、3=大学院卒)
満足度調査(1=不満足、2=普通、3=満足)
このようなデータは、データに何らかの順番付けが必要なときに使います。例えば、製品の顧客満足度を調べたり、病気の重症度を評価したりするときなどです。
間隔尺度とは?
間隔尺度とは、順序尺度に加えて、数字の間に等しい距離がある尺度です。この尺度では、データにつけた数字は、そのデータがどのくらい離れているかを示します。しかし、ゼロという数字は特別な意味を持たないので、数字の比率は計算できません。例えば、次のようなデータは間隔尺度です。
- 温度計(摂氏や華氏)
- 年代(西暦や和暦)
このようなデータは、データの違いが重要なときに使います。例えば、気温の変化を追跡したり、歴史上の出来事を比較したりするときなどです。
比例尺度とは?
比例尺度とは、間隔尺度の特徴に加えて、ゼロという数字が「何もない」や「存在しない」を意味する尺度です。この尺度では、データにつけた数字は、そのデータがどのくらいあるかや、どのくらい大きいかを示します。また、数字の比率も計算できます。例えば、次のようなデータは比例尺度です。
重量(キログラムやポンド)
距離(メートルやマイル)
このようなデータは、実際の量や大きさを正確に測定する必要があるときに使います。例えば、物体の重さを計ったり、走行距離を測ったりするときなどです。
各尺度の違いのまとめ
ここまで、データの種類を分ける方法について、名義、順序、間隔、比例の4つの尺度を説明しました。それぞれの尺度の違いを簡単にまとめると、次のようになります。
この記事を通じて、各尺度の特徴を理解し、データを正しく分析するための基礎を身につけることができたでしょうか。統計学やデータ分析は、データの種類によって使える方法や解釈が変わってきます。データの種類を正しく把握することは、データを活用する上でとても重要です。ぜひ、この記事を参考にして、データの種類を知ることから始めてみてください。