指数と対数について解説します。
多くの専門用語や公式が登場しますが丁寧に理解しやすく説明していきます。
本記事はデータサイエンスを研究されているIffat Maabさんによる英語の解説を翻訳しています。
Iffat Maab
東京大学大学院工学系研究科技術経営戦略学専攻(TMI)博士課程在学中。パキスタン、イスラマバード市出身
マーケターのためのデータサイエンスの時間とは?
こちらの講座では、一般社団法人データサイエンティスト協会様がリリースしている「データサイエンティストのためのスキルチェックリスト」に沿った解説を行っていきます。
「データサイエンティストのためのスキルチェックリスト」とは、データサイエンティストとして活躍するために必要なスキルが体系化されたものです。
このマーケターのためのデータサイエンスの時間に従って学習していくと、データサイエンティストに必要なスキルセットである「データサイエンス力」を一通り学習することが出来ます。
log a(x) の逆関数を説明できる
解答
log a (x)の逆関数は a^xである
(^とは累乗を表しています)
解説
こちらは指数と対数(log)に関する問いです。
まず、指数と対数の違いについて説明します。
指数とは~乗にあたる部分の事です。
対数とはその指数を「指数=」で表すための書き方の事です。
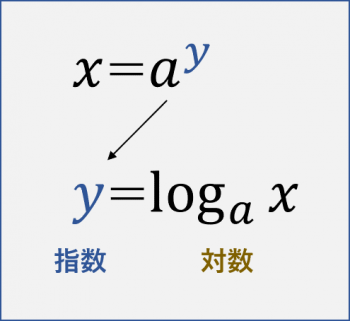
こちらの図では指数はyで、対数はlog a(x)ということが分かります。
それでは、「逆関数」とは何でしょうか?
逆関数とはy=~xの式を、逆にx=の式にで表すことを言います。
例えば、y=2^x である場合にx=の式に変換すると逆関数になります。
つまり、指数と対数の関係性では、指数から見る対数、対数から見る指数が逆関数に当てはまります。
計算過程
loga(x)を y=loga(x)の恒等式に変更します。
逆関数にするために、この式をxについて解きます。
指数を対数に変換する際に、こちらが分かりやすくなっています。
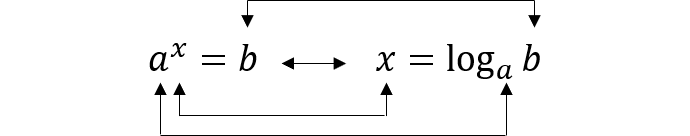
上の図を用いて、
x=a^y となります。
xとyは入れ替えることが出来るため、入れ替えると、
y=a^x となります。
なぜデータサイエンスで指数・対数を用いるのか?
指数・対数は非常に桁数の大きい数値を扱うために用いられています。
例えば、音(デシベル…高い音の尺度)、地震(リヒタースケール)、星の明るさ(非常に高い値)などが挙げられ、これらの数値は桁数が非常に大きく、指数・対数なしでは非常に扱いずらくなっています。
光の速さを指数なしで表すとおよそ、300,000,000km/秒となっています。

引用:写真AC
さらに、上記の数字は理解しにくいだけでなくコンピュータで使用される特定のデータフォーマットに格納するために非常に多くのメモリを必要としてしまいます。
つまり、指数・対数を用いて数字を短くすることで、コンピュータの容量を確保することができているのです。
そこで、指数である10の累乗を用いることで、より簡潔な表記が可能になります。
(光速) 3×10^8 km/秒
このように指数・対数を使うことによって、データ自体を簡略化し、コンピュータが扱えるデータ量を増やすことができます。
おわりに
以上が「データサイエンス力」の基礎となる指数・対数の解説になります。
English
The equation x = 4y is often written as a logarithmic function (called log function for short). The logarithmic function for x = 4y is written as
y = log4 x OR f(x) = log4 x
where y is equivalent to the function f(x)
The number 4 is called the base. In general, y = logb x is read, “y equals log to the base b of x,” or more simply, “y equals log base b of x.” As with exponential functions, b > 0 and b ≠ 1.
Sometimes, there is a need to convert logb x = y to by = x. Other times, you will convert by = x to logb x = y [2b]. In mathematics, the logarithm is the inverse function to exponentiation (power). That means the logarithm of a given number x is the exponent to which another fixed number, the base b, must be raised (power = y), to produce that number x.
Moreover, log is a function of natural log? Natural log is represented as ln(x) and is pronounced as “ell-enn-of-x” The key difference between natural logs and other logarithms is the base being used. Logarithms typically use a base of 10 (although it can be a different value, which can be specified), while natural logs will always use a base of e.
This means:
ln(x)=loge(x)
The example below shows the logarithmic form and the corresponding exponential form.
Another example
In the simplest case, the logarithm counts the number of occurrences of the same factor in repeated multiplications. Since, 1000 = 10 × 10 × 10 = 103, the “logarithm base log101000 = 3” which means 3 times 10 is equal to 1000.
The logarithm of x to base b is denoted as logb(x), or without parentheses, logbx or even without the explicit base, log x, when no confusion is possible like when working with decimal numbers.
Purpose
Now coming towards the purpose of logarithm Much of the power of logarithms is their usefulness in solving exponential equations. Some examples of this include sound (decibel measures… measure of high sounds), earthquakes (Richter scale), the brightness of stars (very high values). If we represent the speed of light or other higher numbers only in digits e.g.,
(speed of light) c = 300000000 (without exponent)
The above number is not only difficult to understand but it also takes more memory for storage in some specified data formats used in computer programming. Hence a more comprehensive and short notation is achieved through the use of logarithmic function which is achieved by changing the powers of 10.
(speed of light) c = 3 108 (exponent form using log)
as natural numbers or decimals it would be hard to understand so we change in the powers of 10
Another example of using the logarithmic function is for measuring the acidity and basic nature of a chemical reaction. Log functions help to represent the acid and basic nature of a chemical through the use of pH balance scale.



